
Trading blocs free#
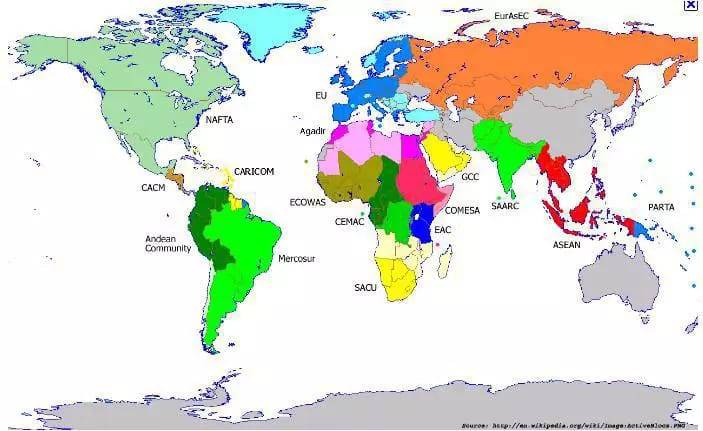
Free trade can lead to structural unemployment as resources shift from uncompetitive industries to newer industries. But, can also have costs for higher-cost domestic producers. This can have benefits in terms of inward investment. Free trade may come at the price of allowing free movement of capital. In a bilateral deal between the US and South-East Asian trading block. Increased influence of multinationals.This may go counter to the particular wishes of a country. A trading block needs to make decisions for the whole area. However, this is almost inevitable even if countries are not formally in a trading block due to a close relationship between trade cycles in different countries. If Eurozone goes into recession, it will affect all countries in the Eurozone. Increased interdependence on economic performance in other countries in trading block.This led to switch in demand towards higher-cost European countries and caused loss of business for Commonwealth countries For example, when the UK joined the EEC customs union, it required higher import tariffs on imports from former Commonwealth countries. Joining a customs union may lead to increased import tariffs – which leads to trade diversion.Therefore domestic firms have a greater incentive to cut costs to remain competitive. The removal of tariffs creates greater choice for consumers. Gives small countries a greater say in global trade agreements.

Gravity theory of trade suggests that trade with countries in close proximity is the most important due to lower transport and similar cultural and economic ties.Countries in Eastern Europe have made considerable progress in catching up with average income levels in Western Europe. Countries joining a rich trading block can benefit from inward investment and increased trade opportunities. Increased trade enables increased specialisation – which gives benefits of economies of scale (lower average costs from increased output).Tariff removal leads to trade creation – lower prices for consumers and greater opportunity for exporters.However, since trade deals are complicated and take several years, there is an advantage to negotiating trade deals as part of a regional trade block – rather than separate individual countries. For example, if imports from Africa enter Spain then if goods travel across the border from Spain to France, there is no need to check whether goods are paying the correct import tariff – because the import tariffs are all the same.Ī disadvantage of joining a customs union is that a country is not able to pursue its own independent trade deals. This means there doesn’t need to be internal checking on ‘ Rules of origin‘. This means that it doesn’t matter which country the imports enter – because all countries have the same import tariff. It has aspirations to become a free trade area.ĭifference between free trade area and customs unionĪ customs union has a common external tariff on imports. Created to forge closer political and economic ties.

Trading blocs full#
Includes full members of Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
